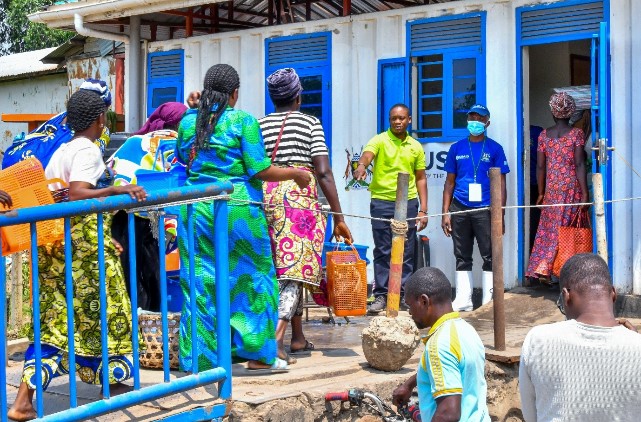
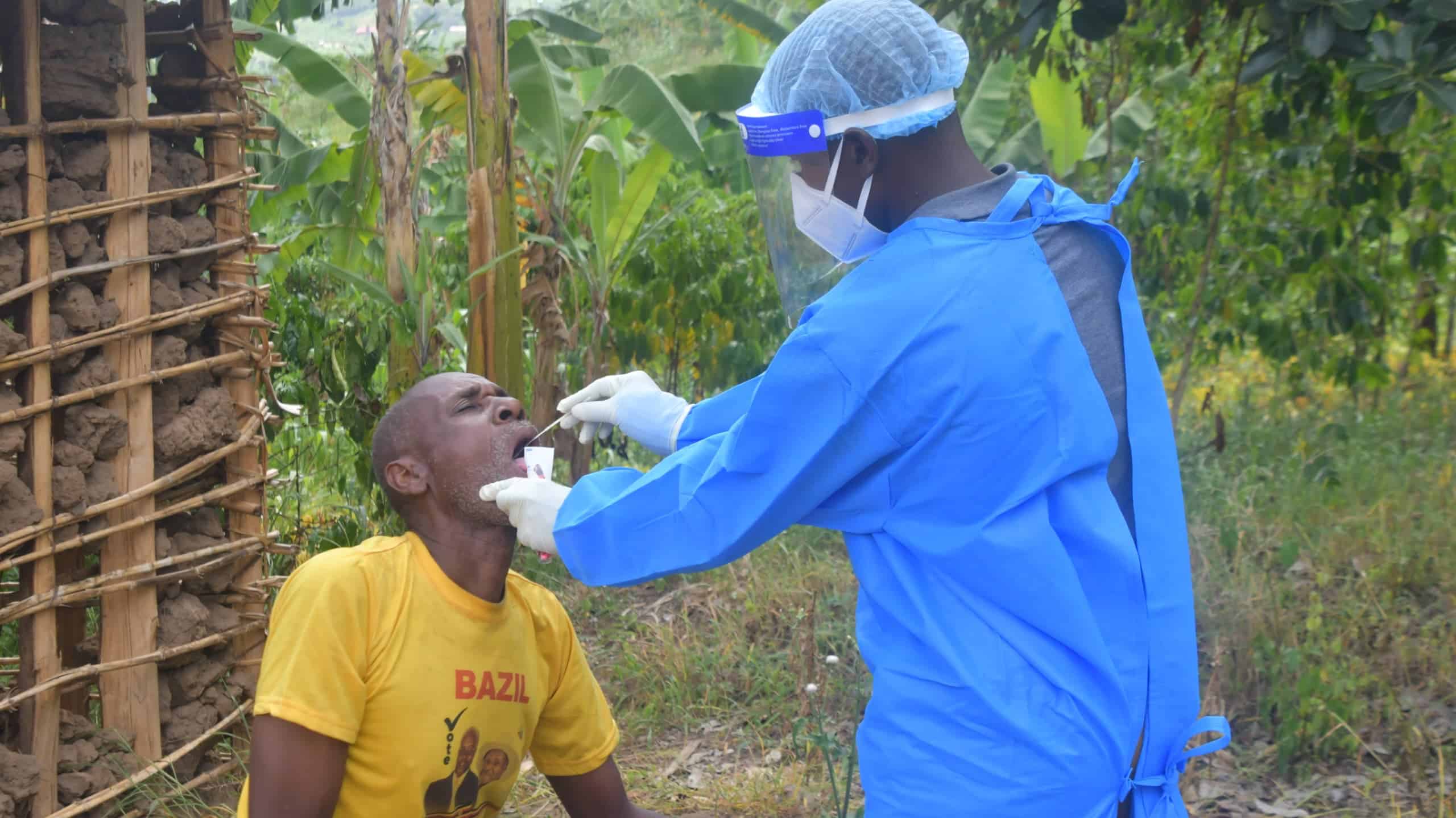
With funding from USAID and Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), we work in support of the Ministry of Health to strengthen border health preparedness at seven border points of entry—Ntoroko Main, Busunga, Kayanzi, Ndaiga, Entebbe, Transami and Busia—offering occasional support to three others—Elegu, Malaba and Mirima Hills.
Enhancing Cross-Border Disease Surveillance through Population Connectivity and Tabletop Exercises
Population Connectivity Across Borders (PoPCAB): Baylor-Uganda led the collection and analysis of population mobility data in high-risk districts for Sudan Virus Disease (SUDV). This initiative supported public health interventions to prevent, detect, and respond to infectious disease threats. Leveraging PoPCAB data, 2,445 trained Village Health Teams (VHTs) successfully traced and followed up with 4,000 contacts—achieving a 91.6% follow-up rate during the Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) response.
Tabletop exercises were conducted at key points of entry— Mpondwe, Busia, Elegu, Malaba, and Mirama Hills points of entry—evaluating and improving Uganda’s capacity for effective cross-border public health response.